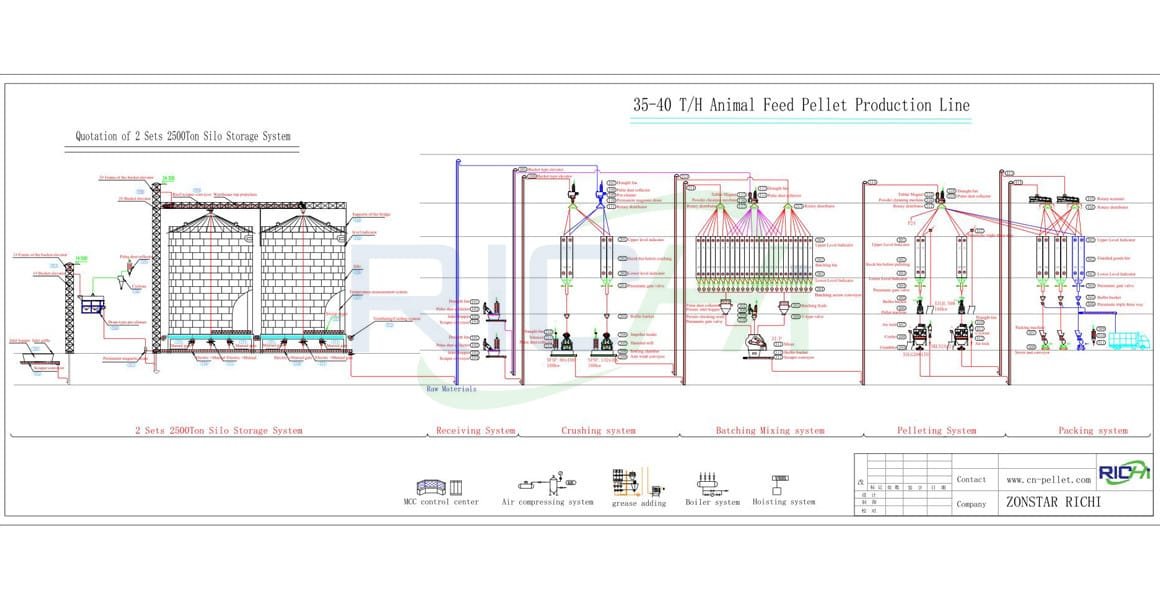
As a professional engineer specializing in the animal feed industry, I frequently get asked about the practical issues that arise when commissioning and operating high-capacity 40T/H feed production lines.
Based on my years of experience, here are some of the most common technical challenges and how to effectively address them:
Particle Size Optimization
Achieving the optimal particle size distribution for ground ingredients like corn, wheat, and soybean meal is crucial for ensuring proper nutrient digestibility and avoiding issues like reduced feed intake.
According to a study by Kansas State University, the ideal geometric mean particle size for poultry diets is around 600-700 microns.
In a 40T/H animal feed line, precision grinding with robust particle size analysis and control is essential. I recommend implementing real-time particle size monitoring with automated adjustment of the hammer mill and roller mill parameters to maintain the target range consistently.
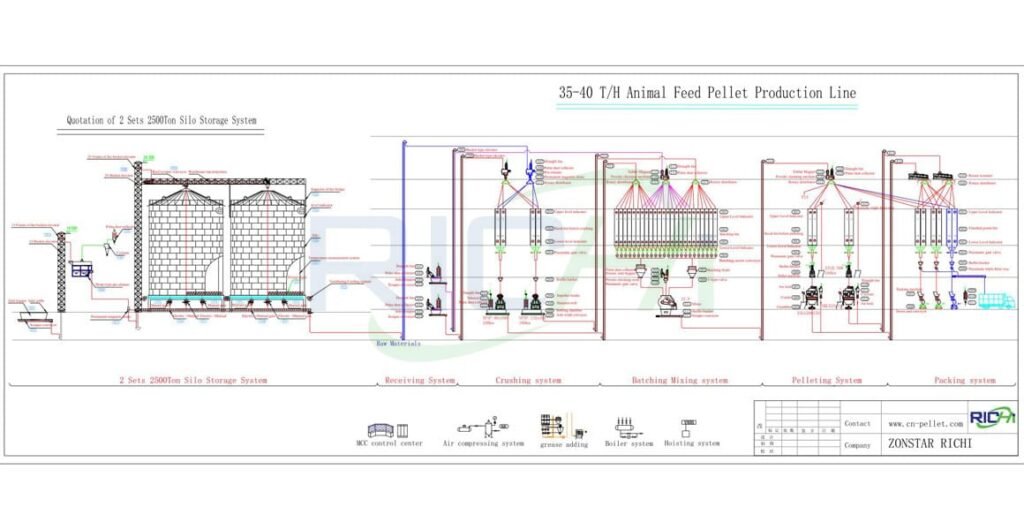
Homogeneous Mixing
Improper mixing can lead to nutrient segregation, resulting in inconsistent feed quality. For large batches in a 40T/H animal feed line, achieving a co-efficient of variation (CV) below 10% for all micro-ingredients like vitamins and minerals is critical, as outlined in the AFIA’s guidance.
Using high-efficiency horizontal ribbon or double-shaft mixers, combined with adequate mix times based on test work, is the key to ensuring homogeneous distribution of all ingredients, including micro-additives at low inclusion rates.
Cross-Contamination Prevention
The risk of cross-contamination between medicated and non-medicated feeds is a major food safety concern in large feed mills. A study by the FDA found that over 25% of investigated cross-contamination incidents resulted in animal health issues.
Implementing robust flushing protocols, physical segregation of product streams, and proper line clearance procedures is essential in 40T/H animal feed production lines handling multiple product types. Automated record-keeping and rigid change-over processes can further mitigate this risk.
Automation and Process Control
With such high production volumes, even minor inefficiencies can result in significant product giveaway and revenue losses. Precise automated process control, from ingredient batching to loadout, is critical for maximizing efficiency and product quality.
I always recommend implementing a comprehensive SCADA system with integrated batch management, providing full traceability and minimizing human errors. Advanced process analytics can further optimize the line performance.
By proactively addressing these common technical challenges through strategic equipment selection, rigorous process design, and robust automation, feed manufacturers can successfully commission and operate large-scale 40T/H feed production lines while ensuring consistent quality, food safety, and operational efficiency.