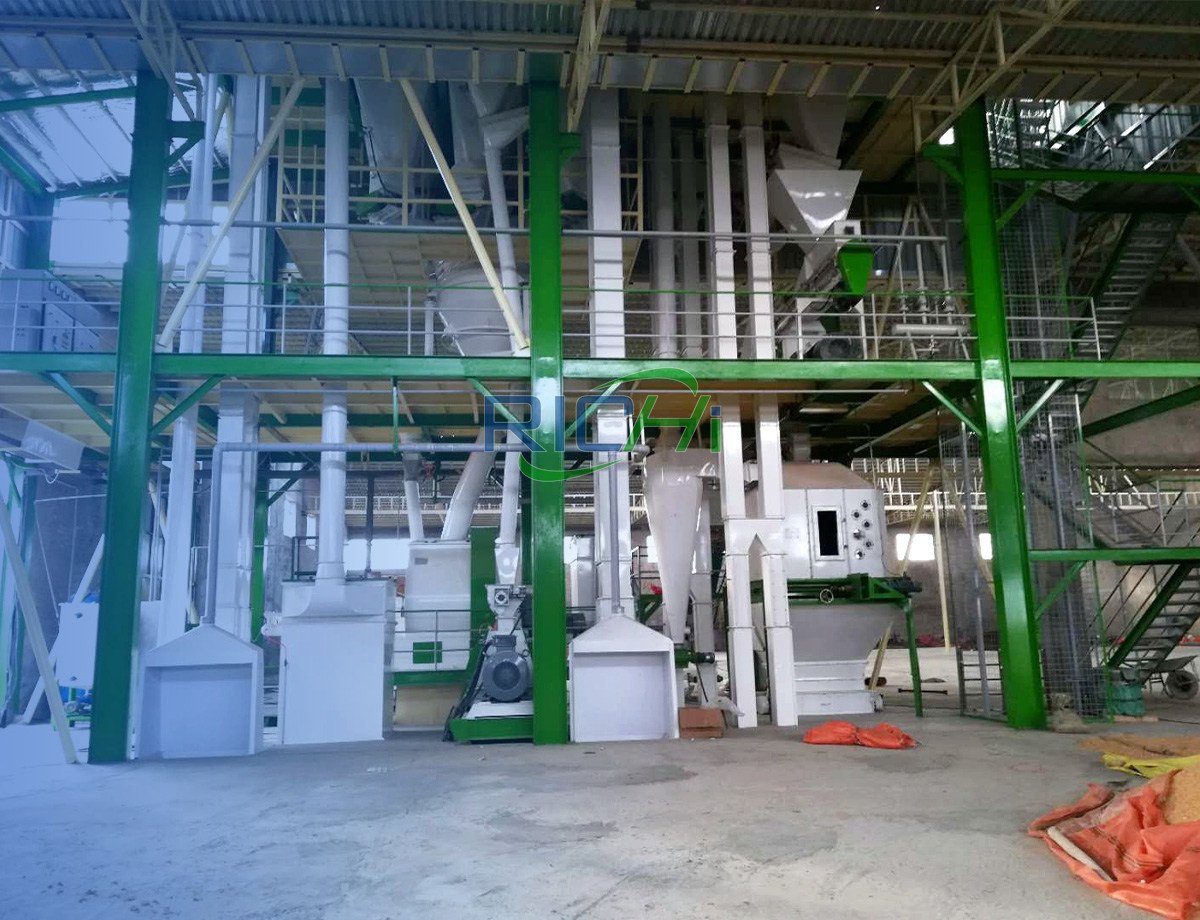
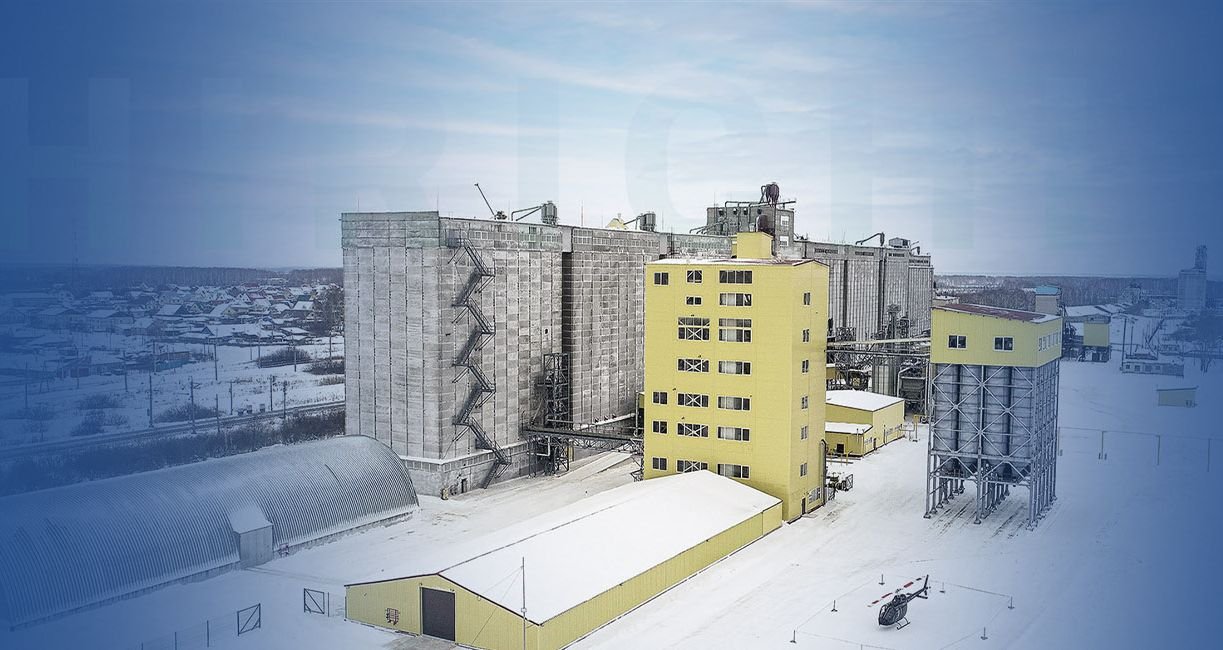
Designing a 5-7t/h animal feed pellet plant involves careful planning and consideration of several key factors to ensure efficiency, quality, and future growth potential. Here’s a detailed guide on what to consider:
1. Production Capacity and Scalability
- Capacity: Ensure the plant can handle a production capacity of 5-7 tons per hour consistently.
- Scalability: Plan for future growth by selecting equipment that can handle slightly higher capacities and by designing modular systems that allow for easy expansion.
2. Raw Material Handling and Storage
- Storage: Design storage facilities to hold at least a week’s worth of raw materials. Consider using silos or warehouses with proper moisture and temperature control.
- Handling System: Implement automated systems for efficient transfer of ingredients to minimize manual handling and errors.
3. Processing Equipment Selection
Grinding Equipment:
- Hammer Mills: Versatile, suitable for a variety of ingredients.
- Roller Mills: Ideal for grains, providing uniform particle sizes.
- Choose equipment that can handle the variety of raw materials used and achieve the desired particle size.
Mixing Equipment:
- Horizontal Paddle Mixers: Efficient for larger volumes and ensuring uniform mixing.
- Vertical Screw Mixers: Suitable for smaller batches or premixes.
- Ensure the mixer is capable of handling multiple batches per hour to support continuous production.
Pelleting Machines:
- Die Size and Thickness: Should match the type of feed produced.
- Capacity: Ensure the pellet mill can handle the 5-7t/h requirement and has adjustable components for different formulations.
Cooling and Drying Equipment:
- Counterflow Coolers: Efficiently cool pellets to the desired temperature and moisture level.
- Dryers: If necessary, ensure they are sized appropriately for the production volume.
Packaging Systems:
- Automated Bagging Systems: For efficient packaging and handling of finished products.
- Accuracy: Ensure systems provide precise weighing and filling.
4. Plant Layout and Material Flow
- Logical Sequence: Design a layout that follows the production flow from raw material intake to finished product storage.
- Minimize Handling: Reduce the distance materials travel between processes to improve efficiency.
- Space Utilization: Optimize vertical space for gravity-assisted material flow and provide adequate access around equipment for maintenance.
5. Quality Control Measures
- In-line Monitoring: Install moisture meters, temperature sensors, and other quality control instruments.
- Laboratory: Set up a lab for testing raw materials and finished products to ensure quality.
- Traceability: Implement systems for tracking raw materials and finished products throughout the production process.
6. Energy Efficiency
- Energy-Efficient Equipment: Use energy-efficient motors and drives.
- Heat Recovery: Implement systems to recover and reuse heat from processes like cooling and drying.
- Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): Optimize energy consumption by adjusting motor speeds according to load requirements.
7. Automation and Control Systems
- Centralized Control: Implement a centralized system for monitoring and managing the production process.
- PLCs and HMIs: Use programmable logic controllers and human-machine interfaces for precise control.
- Manufacturing Execution System (MES): Consider a system for overall plant management to streamline operations.
8. Dust Control and Safety Measures
- Dust Collection: Install efficient dust collection systems to manage dust generated during production.
- Explosion Prevention: Implement systems to prevent and suppress dust explosions.
- Ventilation: Ensure proper ventilation throughout the plant to maintain air quality.
9. Environmental Considerations
- Odor Control: Implement measures to manage odors, especially in plants located near residential areas.
- Wastewater Treatment: Design a system for treating wastewater generated by the plant.
- Noise Reduction: Incorporate noise reduction measures for both equipment and overall plant operation.
10. Regulatory Compliance
- Food Safety: Adhere to standards such as HACCP principles for feed safety.
- Environmental Regulations: Comply with laws regarding emissions, waste management, and other environmental concerns.
- Occupational Health and Safety: Ensure the plant meets safety standards for worker protection.
11. Flexibility in Production
- Versatility: Choose equipment that can handle various feed formulations and ingredients.
- Quick-Change Systems: Implement systems that allow for quick changes to dies and other components.
- Separate Lines: Consider separate lines for different types of animal feed if required.
12. Maintenance and Sanitation
- Ease of Maintenance: Design equipment and layout for easy access during maintenance.
- Cleaning: Use materials and finishes that facilitate thorough cleaning and sanitation.
- Preventive Maintenance: Implement a program to regularly check and maintain equipment.
13. Storage and Logistics for Finished Products
- Storage Space: Design adequate space for finished feed pellets.
- Warehouse Management: Implement a system to manage inventory and facilitate product dispatch.
- Loading Facilities: Consider logistics for truck loading and transportation.
14. Water Supply and Management
- Water Treatment: Design a system for treating water if necessary.
- Recycling: Implement measures to recycle water where possible.
- Pressure and Volume: Ensure sufficient water supply for all processes.
15. Future Technology Integration
- Flexibility: Design the plant to accommodate future technological advancements.
- IoT and Data Analytics: Plan for potential integration of IoT devices and data analytics for process optimization.
- Automation: Consider future needs for increased automation and robotics.
16. Staff Facilities and Training Areas
- Workspaces: Design comfortable and efficient work areas for operators and supervisors.
- Training Facilities: Include areas for staff training and development.
- Amenities: Ensure adequate facilities such as restrooms, locker rooms, and break areas.
17. Biosecurity Measures
- Separation: Maintain clear separation between raw material and finished product areas.
- Biosecurity Facilities: Include areas for staff and visitor biosecurity procedures.
- Quarantine Areas: Plan for quarantine or isolation areas if needed.
18. Backup Systems and Redundancy
- Power Backup: Install backup power generators to ensure continuous operation.
- Equipment Redundancy: Consider redundancy in critical equipment to minimize downtime.
- Data Backup: Implement robust data backup and recovery systems.
Conclusion
Designing a 5-7t/h animal feed pellet plant requires a comprehensive approach to ensure efficient and reliable operation. By addressing factors such as equipment selection, plant layout, quality control, energy efficiency, and future scalability, you can create a facility that meets current production needs and is well-positioned for future growth. Balancing production efficiency, product quality, regulatory compliance, and environmental impact will help ensure the long-term success of the plant.
Related post: small scale feed mill